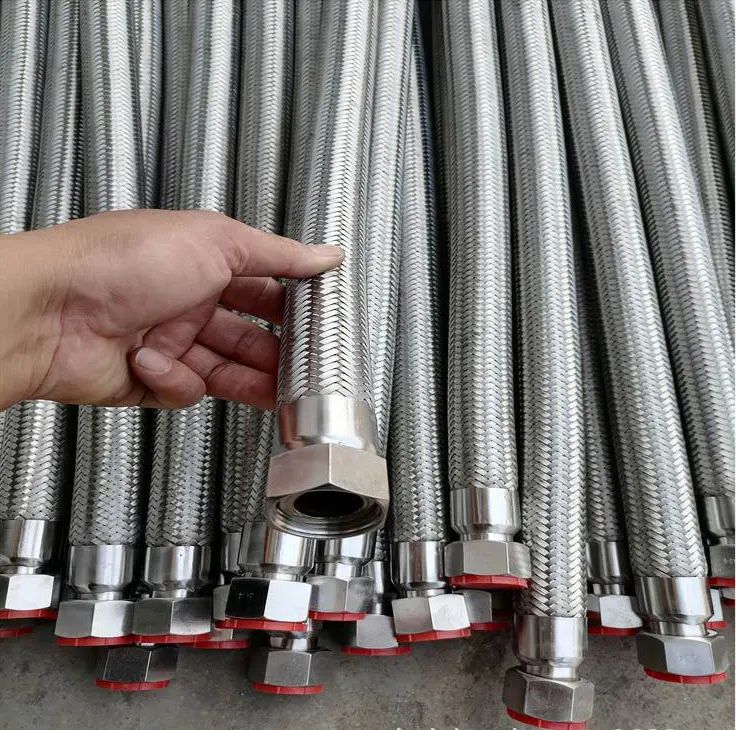
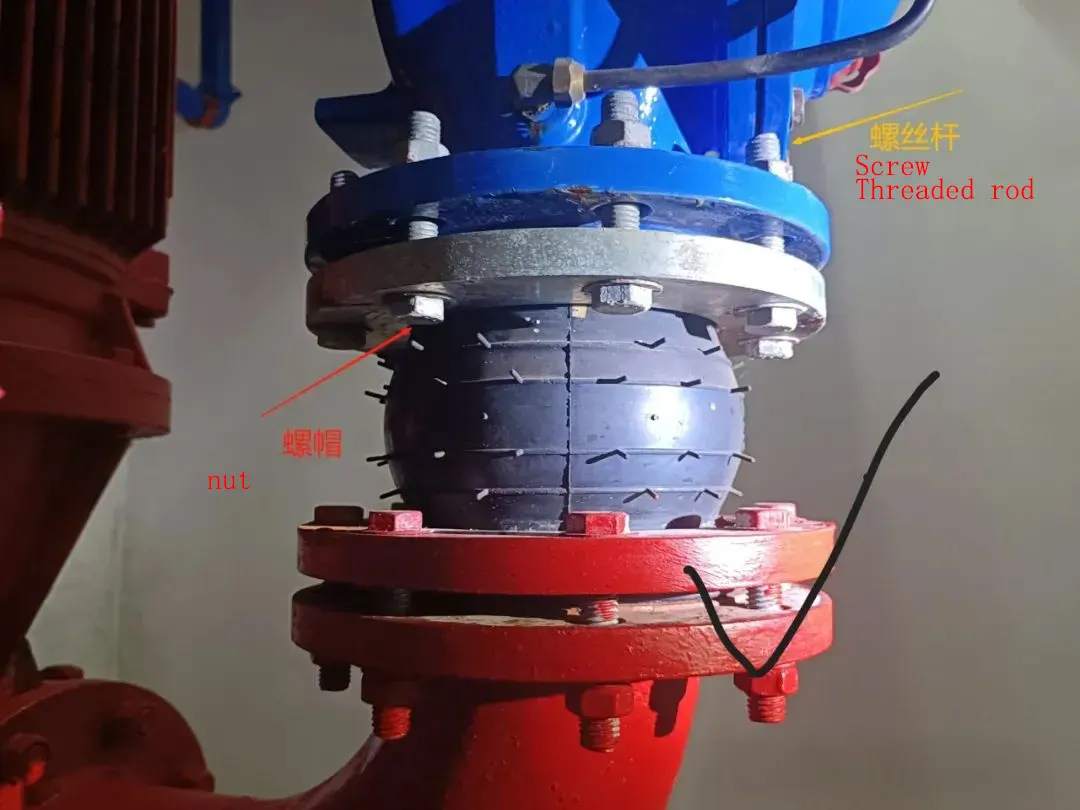
Within a fluid carrying system, the pivital machinery is a centrifugal pump and its proper functioning influences the dependability of the entire process chain. Metal hoses maintain their importance, as the connecting parts of the centrifugal pump inlet and outlet pipelines, the self-perception as the standards of hose connection, the style of post operational maintenance, and post usage surveillance tend to become the hidden variables that greatly influence the operational life of pump units and the integrity of the entire system. With these variables taken into consideration, the current piece of writing identifies the steps that an on site engineer should take when carrying centrifugal pumps and providing further operational strategies.

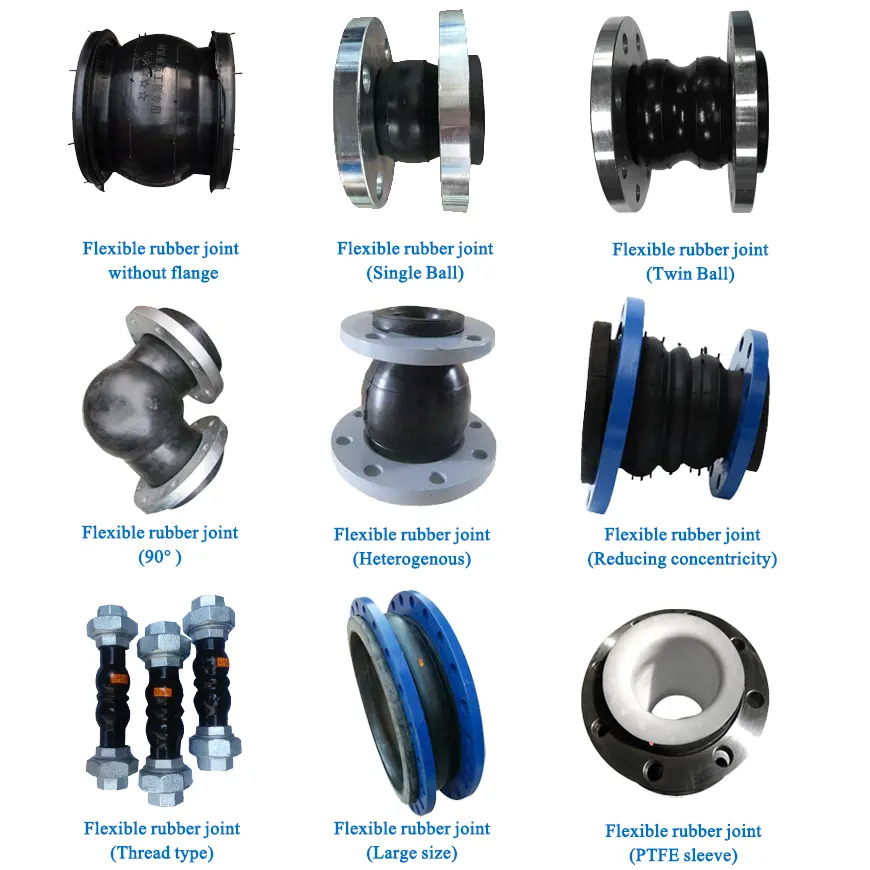
1) Selection: Match Service to Specs and Prevent “Built-in” Mismatch
While operating centrifugal pumps, the equipment sustains some form of vibrations as well as expansion, contraction, and even some installation deviations. The principal role of metal hoses is to maintain fluid sealing and absorption of some of the displacements. The neglect of some critical parameters during the selection stage can easily lead to abnormal vibrations of pump units as well as early failure of the hoses. The impact of the following dimensions should be closely monitored:

1.1 Pressure rating: apply a 1.2× safety factor
The rated working pressure of the metal hose must cover the design pressure plus the pressure fluctuation peak of the centrifugal pump, plus an additional 1.2x safety factor. To illustrate, if the design outlet pressure of a centrifugal pump, for example, for the conveying of clean water is 1.6Mpa, considering the water hammer effect during startup and shutdown, a pressure fluctuation which may reach 2.0Mpa, a metal hose with a rated pressure of no less than 2.4Mpa (2.0 × 1.2) should be selected. As a word of caution, the bellows material (304/316L), the number of layers (1 layer/2 layer), and the mesh structure (steel wire/steel strip) determine, to a great extent, pressure-bearing capacity. The combination of 316L material + 2 layer steel wire mesh is most advantageous for the corrosive operating conditions.

1.2 Movement capability: match pump vibration and piping offsets
The inflexible coaxiality of installed pipelines and operational centrifugal pump radial and axial stroking displacement during centrifugal pump operation pump vibrational displacement must be compensated by the capacity of the metallic hoses. Before the hoses are selected, the following two primary parameters must be quantitatively measures on-site or defined by the pump type handbook:
- Radial Displacement: Typical ranges for centrifugal pumps positioned horizontally are 0.5–3mm whereas pumps positioned vertically due to the difference in geometrical structure are 5mm axial radial displacement. The radial displacement of the metallic hose must be greater than or equal to 1.5× the measured value.
- Axial Displacement: The axial thermal expansion and contraction of pipelines is caused by heat and can be measured by the formula ΔL = α × L × ΔT, whereby in the given formula, α is the linear expansion of the pipeline, L is the length of the pipeline, and ΔT is the different temperature. The hose must possess axial compensating value in excess of the computed value.

1.3 Media compatibility: prevent corrosion-driven failure
Selecting hose materials should depend on the type of medium and its temperature range.
- For normal clean water and lubricating oil: bellows of stainless steel 304, and steel wire mesh, temperature range: -20 to 300 degrees.
- For medium that has a corrosive effect (e. g. acid – base solutions): 316L stainless steel and or Hastelloy bellows with nickel alloy mesh.
- For medium that has high temperature (for example: steam or hot oil): the hose needs to have a lining of PTFE and the temperature resistance of the hose needs to be greater than the working temperature of the medium.

2.Installation: Details Drive Seal Integrity and Service Life
The installation of metal hoses should always be done with care since any rough installation may result in the performance and service life of the hose greatly suffering. On site construction has to follow the set instructions below strictly, in order to avoid hose damage or leakage, which are caused by improper procedures:
2.1 Coaxial alignment: never “force-fit”
Guidelines set the coaxiality of the centrifugal pump inlet and outlet and the associated pipeline flanges must be set and monitored so that they do not exceed φ0.5mm, with the end face sombrerete not exceeding 0.2mm/m. Before installation, the coaxiality of the two flanges has to be measured with dials. If the dials show an alignment that are not the same norm, using any form of ‘forced alignment’, stretching or wrench to a metal hose is ‘vehemently discouraged’. While people may think that this may result in a permanent deformation to the hose, the truth is this increases the chance of hose having seal leakage and rupture in the long run. Other than this, people must be highly encouraged to adjust the positions of pipeline supports, or even select metal hoses that have universal joints in order to help on the deviations which are through the joints.
2.2 Installed length: leave “movement margin”
The design length of the hose may not exceed or fall short by 5% to maintain the restraints below:
- Too short: Fails to accommodate the vibration of the pump unit as well as the thermal expansion and thermal contraction of the hose, which results in additional tension on the hose, as well as uneven and unbalanced stress on the sealing surface which then leads to leakage;
- Too long: Failure of the hose under the impact of fluids, which results in the deformation of the hose, causes the issue of hose bending under the weight of itself, which in turn, causes damage to the bellows and deformation of the pipeline.
The hose length can be adjusted by using a tape measure placed around the hose. In the case of a hose that isn’t too long, the increase or decrease of adjusting the bolts leads to the reduction or increase of the diameter of the flanges which results in the length of the hose also decreasing or increasing.

2.3 Restraint and support: avoid “free-hanging” loads
Metal hoses have no independent load-bearing capacity. After installation, the pipeline must be fixed at both ends of the hose and suspended pipelines. Otherwise, the hose might have to suspend the weight of the fluid and the pipeline:
- For the horizontal installation of the pipeline: the distance between supports must be ≤ 1.5× the pipeline diameter, and the distance between the support and the hose must be ≥ 100mm, to avoid support contact with the hose surface;
- For the vertical installation of the pipeline: Any suspension device must have a vertical load-bearing support below the hose, or the belt may be considered; “anti-sagging ” supports must be added in the intermediate sections of the hose. These must prevent the hose from stretching under self-weight due to the hose stretching under self-weight;
- Intermediate hose sections close to the pump body: To minimize shock and other dynamic pump unit vibrations transferred to the hose, a rigid support must be placed not more than 300mm from the pump flange.
2.4 Sealing & bolting: control torque, cross-tighten
For sealing surfaces, appropriate gaskets must be chosen (nitrile rubber gaskets for oil, PTFE gaskets for acid and bases, etc.). Bolts must be tightened according to “diagonal uniform tightening” and controlled torque must be applied:
- For M16 bolts (304 material): Tightening torque is 45–55N·m;
- For M20 bolts (304 material): Tightening torque is 80–90N·m;
If torque is too low, the sealing surface may leak due to insufficient 贴合; if too high, the flange sealing surface and hose flange may be torqued to the point of sustained deformation. A torque wrench is the recommended tool for controlled torque tightening, post which uniform flange gap and lack of deflection must be checked.

3. Maintenance: Scheduled Inspection and Diagnosis, Increase System Lifespan
Post-operation maintenance of metal hoses is of great importance for uninterrupted functioning of centrifugal pumps. A mechanism for periodical checks must be developed to detect and act on possible failures in a timely manner to avoid minor faults to contribute to phon events of the system:
3.1 Daily Inspection: Concentrate on “Leakage and Vibration”
The indicators below are needed for daily inspections:
- Covering on Equipment: The hoses and Flanges should be checked for leakage. If leakage is detected, ascertain if the gasket is old or if the bolts are loose. If the bolts are loose, retighten them to the correct torque. If the gasket is old, the system will need to be deactivated to replace the gasket; while doing the replacement make sure to scrub impurities on the sealing surface to prevent the sealing from being badly affected.
- Vibration Level: Vibration Detectors should be used on the compressors to measure the amplitude perpendicular to the equator. Vibration amplitudes of hoses on centrifugal pumps should not exceed 2.8mm/sec. If the set point is exceeded, determine if the centrifugal pump set is out of balance or if the hoses are installed excessively, and are causing resonance.
- Infrared Inspection: Check the upper part of the bellows for rust, scratches, dents, or broken wire meshes. If rust is found, try to sand polish and then coat with primer. If the broken wire meshes is more than 3 per meter, the hose should be replaced.

3.2 Regular Testing: Maintain Cyclical Completion of the “Performance Verification” Procedure
Full inspection of the metal hose is recommended every six months:
- The operator closes the outlet valve of the centrifugal pump and begins to inject clean water into the pipeline. The hose is subjected to a constructive cleaning and is then pressured at a ratio of 1.2x. 1.1. The water is kept at a hose pressure of 30 units for 30 minutes. If the pipe keeps pressure and is hose leak free, the hose is pressure bearing capable;
- The centrifugal pump is engaged while using a determining dial to capture the recessed and prominent spans of the hose. If the total distance of the bounding spans exceeds the calculated value while the pump operates, there is then a loose structure of pipeline supports plumbed to the pump;
- If the application of corrosive operating conditions is applicable, the material composition of a particular bellows can be checked and tested using the material composition spectro analyzer. If the material composition and spell checking braches indicate and capture a 5 percent deviation, the hose then requires replacement.

3.3 Troubleshooting: ‘Quick Solutions’ for Common Problems.
| Fault Phenomenon | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Leakage at Flange Connection | 1. Insufficient bolt torque; 2. Gasket aging; 3. Flange surface deformation | 1. Re-tighten bolts according to standard torque; 2. Replace with gaskets of the same material; 3. Polish the flange sealing surface, replace the flange if damage is severe |
| Rupture in the Middle of the Hose | 1. Forced twisting during installation; 2. Fatigue caused by excessive vibration; 3. Medium corrosion | 1. Replace the hose and re-calibrate flange coaxiality; 2. Add pipeline supports to reduce vibration; 3. Replace with corrosion-resistant hoses |
| Significant Pressure Drop | 1. Internal blockage of the bellows; 2. Reduced pressure resistance due to broken mesh | 1. Dismantle and clean the hose, replace if blockage is severe; 2. Check the mesh condition, replace the hose if wires are broken |
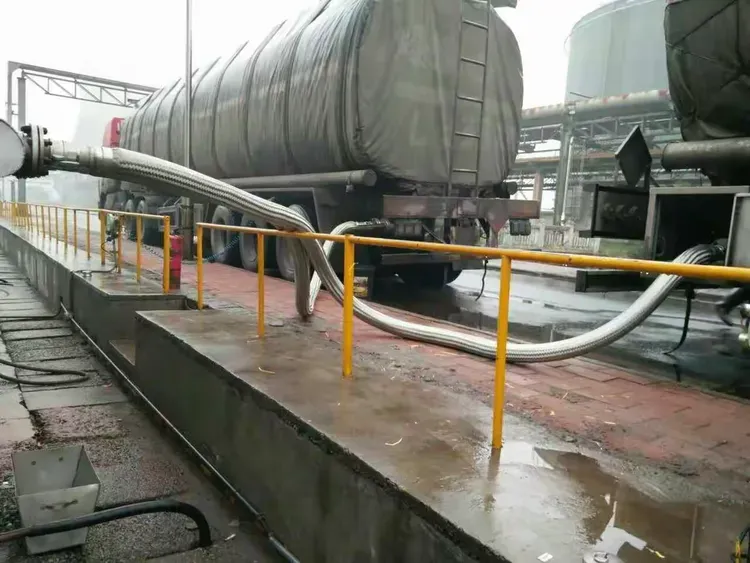

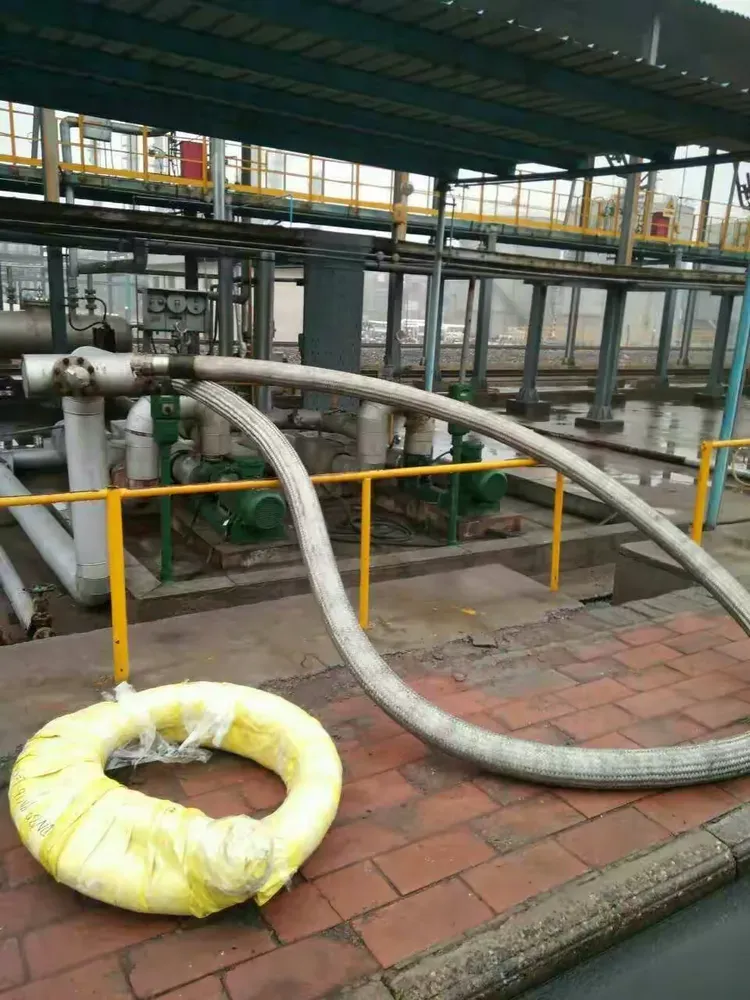
4.Engineering Case: From Problem to Optimization. Witness Technical Implementation Effects
A centrifugal pump sending system in a chemical enterprise (medium: 30 percent sulfuric acid solution at 80C) had pumps with a lot of leaky metal hoses and this made it so they needed 2 or 3 replaced every month. This was really impacting the productivity. From the field study, we found:
- Misdiagnosis: Initially, 304 stainless steel hoses were chosen which are not capable of withstanding sulfuric acid corrosion, causing pronounced rust within the bellows;
- Divergence from the plan: Horizontal offset of the centrifugal pump flange and the pipeline flange was φ2mm, and hose stretching forced alignment which deformed the bellows;
- Neglected Consequence: The poorly designed hose was installed upright, and because of its unsupported weight, the hose was allowed to sag freely causing unequal stress to the hose sealing surface.
Compliance plan:
- Selective replacement: Chose breathers with PTFE+SUS304 stainless steel bellows + SUS304 nickel alloy mesh, capable of 2.5MPa, withstanding -40℃ to 400℃, and sulfuric acid compatible.
- Realignment: Added pipeline supports to flange coaxiality, keeping the deviation within φ0.3mm, and 100mm hose length was removed to alleviate resonance.
- Added support: Installed mid-hose sag clamps along with bottom supports to axle to ensure the hose does not freely suspend and carry load.
The ongoing optimization of the metal hoses in the system improved its service life from 1 month to 18 months, eliminated the leakage rate, and annual maintenance downtime was streamlined by 60 hours, thus saving maintenance costs of over 100,000 yuan.

Conclusion
Although the connection between metal hoses and centrifugal pumps has an air of simplicity about it, it is, in fact, an exceedingly important connection in the fluid system. It is akin to the proverbial saying, ‘the touch that moves the whole system’. Every single step from the parameter verification during selection to the detail control during the installation, all the way to the regular testing during maintenance, is the work of engineers who are mechanically precise in their technical drawings. They understand the control and feedback loops. There are three of them: ‘operating condition matching’, ‘precision installation’, and ‘proactive maintenance’. The whole purpose is to ensure that the metal hoses functioning to their utmost capacity, the centrifugal pumps are guaranteed to work in a stable manner. This lays a firm base for the entire fluid conveying system and thus, it is able to rely on its centrifugal pumps for the fluid system to work continuously.