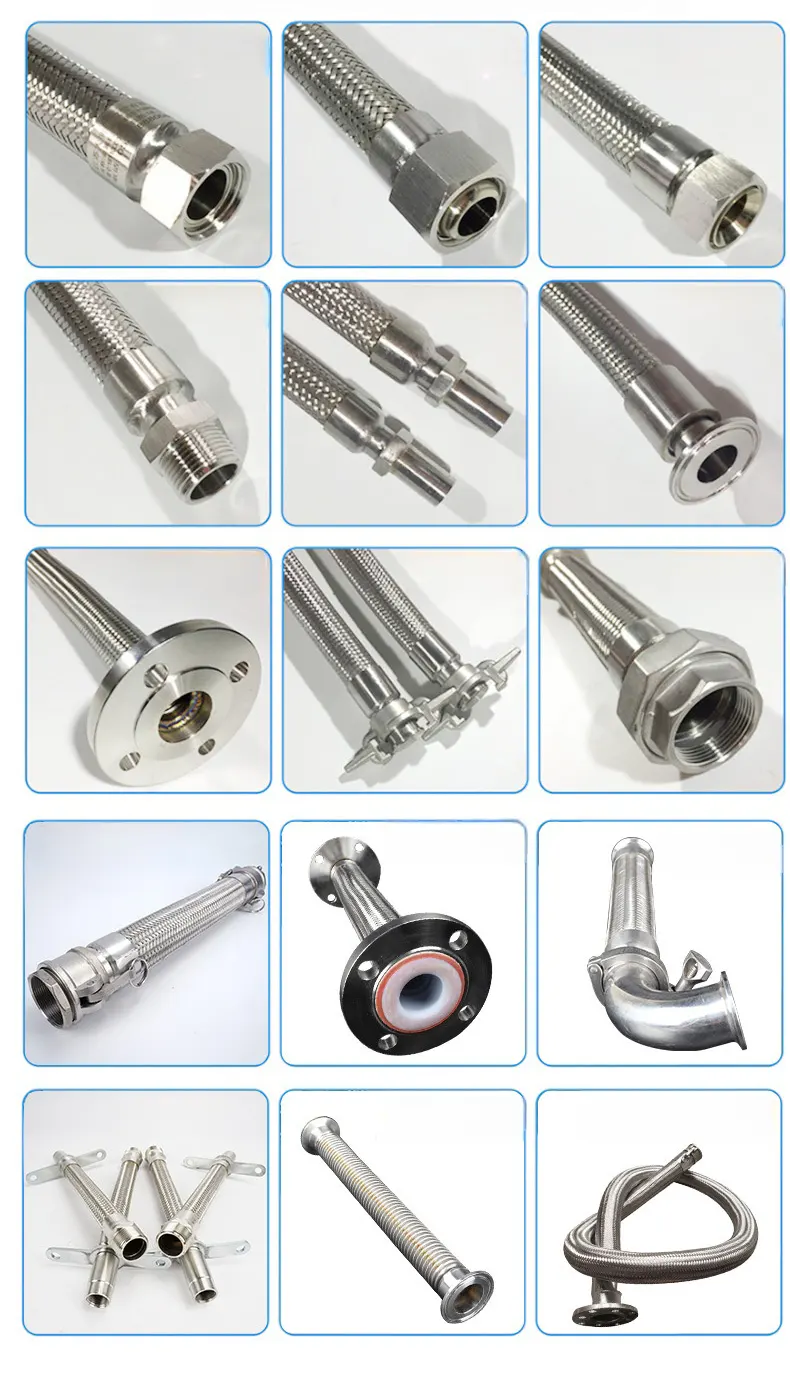
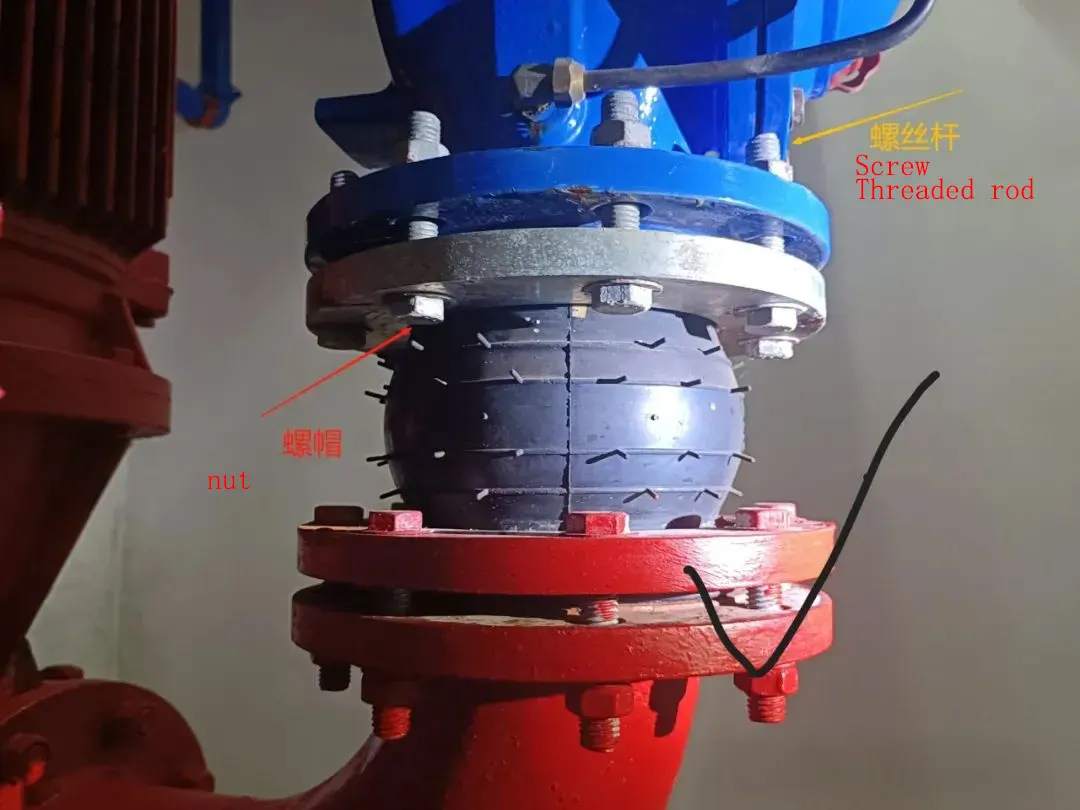
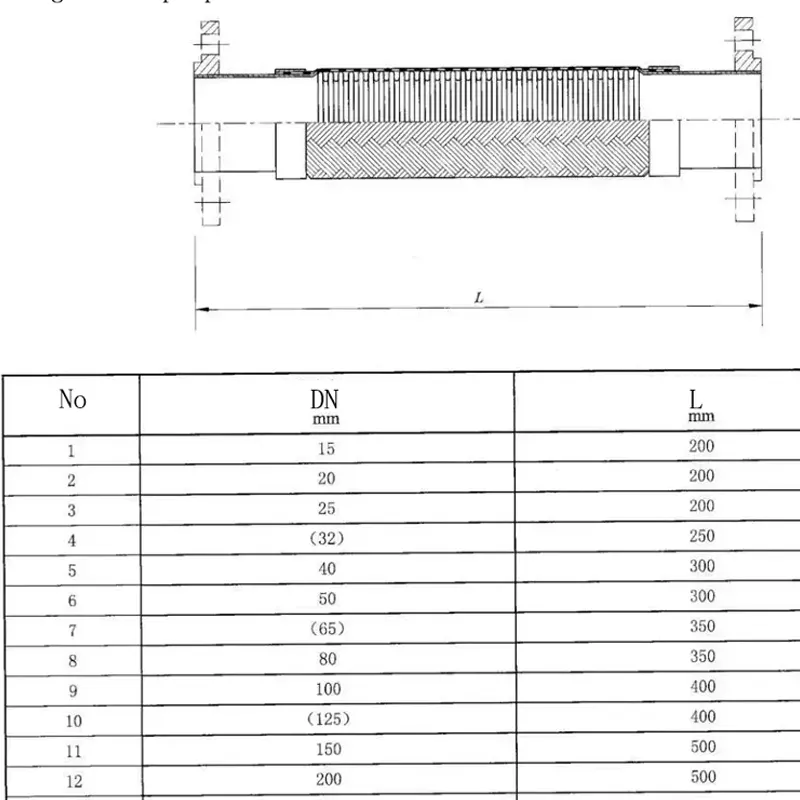
Metal hoses are critical flexible connectors in modern industrial piping systems. They generally consist of three main parts: the bellows, the braid, and the end fittings.
The bellows form the body of the hose and provide flexibility. They can bend freely, and the internal stress generated within the rated bend radius is minimal, which greatly simplifies installation while helping ensure the safe operation of the piping system.
Metal hose has a long history. Early flexible conduits were stitched from animal hides. With the advent of rubber and vulcanization, rubber hoses and armored rubber hoses appeared. However, rubber could not meet requirements for high/low temperatures or corrosive media. Attention turned to metal tubing, and through continuous improvement and technological advances, metal bellows were developed, leading to today’s wide variety of metal hoses.
2. Materials Used in Metal Hoses

(1) Common Material Options
Metal-hose flanges are typically either slip-on flanges or lap-joint (loose) flanges.
Slip-on flanges are commonly used on shorter runs; materials include carbon steel, cast steel, and stainless steel. Lap-joint flanges are used on longer runs to compensate for bolt-hole misalignment over long distances.
Bellows are most often made from stainless steels such as 304, 316, and 316L, which offer good pressure resistance, wide temperature tolerance, corrosion resistance, and fatigue resistance.
The braid is usually woven from 201 or 304 stainless. Under operating pressure, the braid carries hoop load and protects the bellows. Depending on pressure and the service environment, one or more layers of stainless wire or strip may be braided.
(2) Characteristics and Suitable Scenarios
Carbon-steel flanges are relatively low cost but offer poorer corrosion resistance than stainless steel. They are suitable for general industrial environments where corrosion is not a major concern. Cast-steel flanges have higher strength and can handle moderate pressures, making them appropriate for mid-pressure connections.
Stainless-steel flanges, bellows, and braids exhibit strong corrosion resistance and remain stable in a wide range of aggressive media. For example, in petroleum and chemical applications, stainless-steel metal hoses perform excellently. Their working temperature range is very broad, from −196°C to 600°C. They function reliably in both deep-cryogenic media such as liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen and in high-temperature steam service.
304 stainless-steel hoses combine good corrosion resistance with high-temperature capability, making them suitable for most general industrial and civilian uses (e.g., wire and cable protection or shower hoses). 316 and 316L stainless-steel hoses offer superior corrosion resistance, especially in marine and harsh chemical environments.
Braids woven from 201 or 304 stainless wire or strip increase crush and pressure resistance while protecting the bellows from mechanical wear. The number of braid layers can be selected according to system pressure and safety requirements.
3. How to Select a Flexible Metal Hose

(1) Key Parameters to Consider
1. Nominal diameter (DN): Determined primarily by the equipment and flow requirements. Precision instruments may require smaller DN; large industrial piping typically needs larger DN. Without this parameter, other selections lose meaning.
2. Medium: Select materials according to the chemical properties of the conveyed media. For example, 201 stainless is comparatively poor in corrosion resistance; 304 tolerates mild acid/alkali; 316 is stronger overall, though even 316 is not universally resistant to all strong acids.
3. Operating temperature: Although often overlooked, it matters. Stainless steel service limits are commonly cited up to ~600°C, but you should choose materials to match real-world operating and ambient temperatures to avoid overheating or embrittlement at low temperature.
4. Working pressure: A critical parameter driven by equipment/system pressure. As a rule of thumb, for a given construction the larger the diameter, the lower the pressure rating. For special high-pressure or pulsating-pressure applications, multiple braid layers are often required to increase pressure capacity.
(2) Quick Checks on External Quality
By touching the hose surface you can make an initial quality assessment. If it feels rough or “splintery,” quality is usually inferior. High-quality metal hoses feel smooth and even.
You can also observe the bellows and braid surface. After rubbing by hand, if there’s no dark smudge and the surface appears gray, the wire may be an alloy; if the surface is black and glossy it may be stainless wire, while a chalky, dull white appearance can indicate other alloy wires. In general, stainless content correlates with more practical durability.
Check the gap and pitch between individual wires: smaller, more uniform gaps typically indicate a denser weave and better quality. Also inspect other accessories and materials. Smell the plastic drain/port area: poor-quality plastics can emit a strong odor; higher-quality products generally do not.
(3) Choosing a Reliable Manufacturer
Selecting a trustworthy and capable manufacturer is essential. The market includes many vendors with varying quality and reputation. Consider:
- Product quality: Top manufacturers invest in raw-material selection and process control to ensure corrosion resistance, high-temperature/pressure performance, and consistent reliability across environments.
- Safety and service life: High-quality hoses last longer and improve safety, preventing accidents caused by inferior products.
- Reputation: User reviews help reveal performance in product quality and after-sales support. Reputable manufacturers tend to excel in quality, on-time delivery, and service attitude.
In short, weigh quality, reputation, and after-sales support together to ensure you purchase a high-quality hose.
4. Features of Metal Hoses

(1) Performance Highlights
Metal hoses offer many advantages. First, corrosion resistance: since the key components are austenitic stainless steels, you can select specific grades according to the conveyed medium. Whether in corrosive environments in oil and chemical industries or in harsh marine conditions, metal hoses operate stably.
They also excel at both high and low temperatures, typically handling −196–600°C. For instance, they work reliably in cryogenic media like liquid hydrogen and oxygen, as well as in high-temperature steam.
304 stainless may be used up to about 450°C, while 316-series products can reach ~600°C, and 316L is sometimes quoted up to ~700°C under certain conditions.
Low weight and compact size make installation easier and reduce load on equipment and piping. The hoses are very flexible—with strong elasticity, bendability, and vibration resistance.
Pitch-to-pitch flexibility is high, minimum bend radii are small, and there is no blockage or stiffness. Unit weight is low, diameters are consistent, and they withstand repeated bending. Tensile and side-load resistance is strong; the hose feels smooth and is easy to pull cables through and position during installation. These qualities suit complex routings and challenging environments.
(2) Structural Advantages
Metal hoses generally comprise bellows, braid, and fittings. The bellows—thin-wall stainless tube formed hydraulically into helical or annular corrugations—provide the key flexibility with low added stress at the rated bend radius.
The braid, woven from crossing metal wires or strips, is mounted over the bellows to provide reinforcement and shielding, giving the assembly a higher pressure rating.
Fittings are broadly threaded, flanged, or quick-connect. Depending on requirements, the bellows, braid, and fittings are joined by welded, mechanical clamping, or hybrid methods.
This structure makes metal hoses suitable for rotary-joint interfaces and for flexible connections conveying a wide range of media. They are widely used in aerospace, petroleum, chemicals, metallurgy, power, pulp and paper, lumber, textiles, construction, pharmaceuticals, food, tobacco, and transportation.
5. Applications of Metal Hoses

(1) Industrial Applications
In aerospace, metal hoses act like the “arteries and veins” of the vehicle, routed through critical paths to deliver fuel and pressurizing gases. During rocket operation, the hose’s unique combination of flexibility (to absorb vibration-induced deformation and displacement) and stiffness (to withstand high alternating loads) ensures robust connections.
For example, during the launches of the Long March-2F Y13 and Shenzhou-13, metal hoses developed by Aerospace Morninglight Co., Ltd. handled complex loads and extreme temperatures, reliably delivering propellants into the combustion chambers and contributing to mission success.
In oil and petrochemicals, metal hoses commonly convey high-temperature, high-pressure media such as crude and chemical products. Their resistance to heat, corrosion, and pressure enables stable operation under extreme conditions. Flexibility also eases installation in complex layouts while maintaining reliable connections.
In metallurgy, metal hoses are used for cooling and heating circuits that involve high-temperature, high-pressure media. Flanged hoses are widespread here; robust outer protection and suitable coating systems help ensure dependable performance.
Metal hoses also compensate for pipe movement. Beyond pressure and temperature, industrial systems face fatigue, corrosion, vibration, crushing, and impact. Metal hoses shine in these combined conditions, absorbing movement, reducing system vibration, improving fatigue resistance, and lowering noise.
(2) Daily-Life and Building Services
In civilian use, metal hoses serve as shower hoses, with sizes from DN 3 to DN 150 to meet diverse needs. Small-bore hoses (DN 3–25) protect sensor lines for precision optical instruments and industrial sensors, and safeguard wiring in household appliances.
In high-rise buildings, large-diameter metal hoses can be applied in drainage, ventilation, and heating systems, adapting to complex structures and conditions to ensure reliable operation. Small-bore hoses with an additional woven braid provide better performance—corrosion resistance, heat resistance, oxidation resistance—and longer service life for residential and public piping connections.
For household gas connections, metal hoses are increasingly preferred. Traditional rubber gas hoses age easily and can detach, posing safety risks. Metal hoses offer better overall performance, resist aging, and form more secure joints—helping to prevent gas accidents and provide a safer, more reliable supply at home.

6. Purchasing Checklist (Key Takeaways)
When selecting a metal hose, consider the following to ensure the product fits your needs:
- Size: Determine nominal diameter (DN), choose fitting type (flange, threaded, or quick-connect), and confirm the effective hose length based on installation needs—especially in tight spaces.
- Pressure: Based on actual working pressure, consult DN vs. pressure ratings and decide whether a stainless-steel braid (single or multiple layers) is required. Higher pressures generally call for multiple braid layers.
- Medium: Match the hose body and accessories to the chemical characteristics of the medium. For corrosive media, avoid carbon-steel interfaces; choose stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials.
- Temperature: Select materials for the full operating temperature range of the medium; note that different materials have different limits (stainless steels often cited up to ~600°C).
- Service conditions: Select appropriate flexibility and minimum bend radius and install correctly to avoid leakage. For frequent bending, choose higher-flexibility bellows and verify bend radius and support spacing.