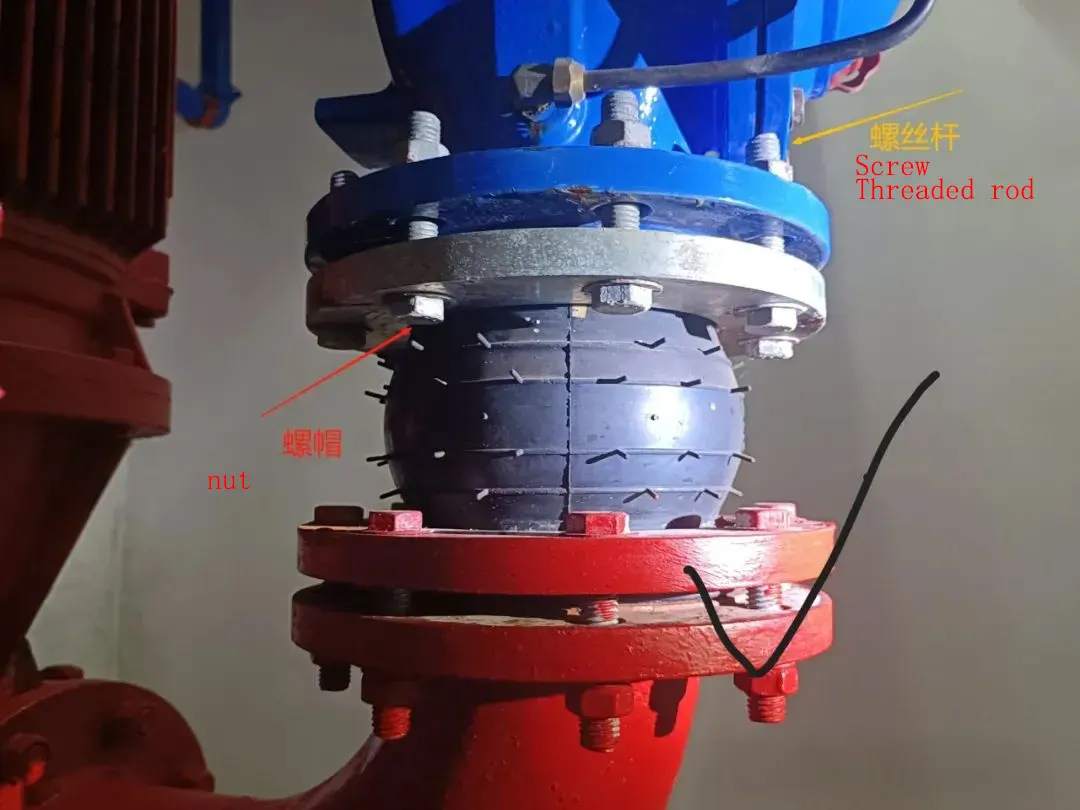
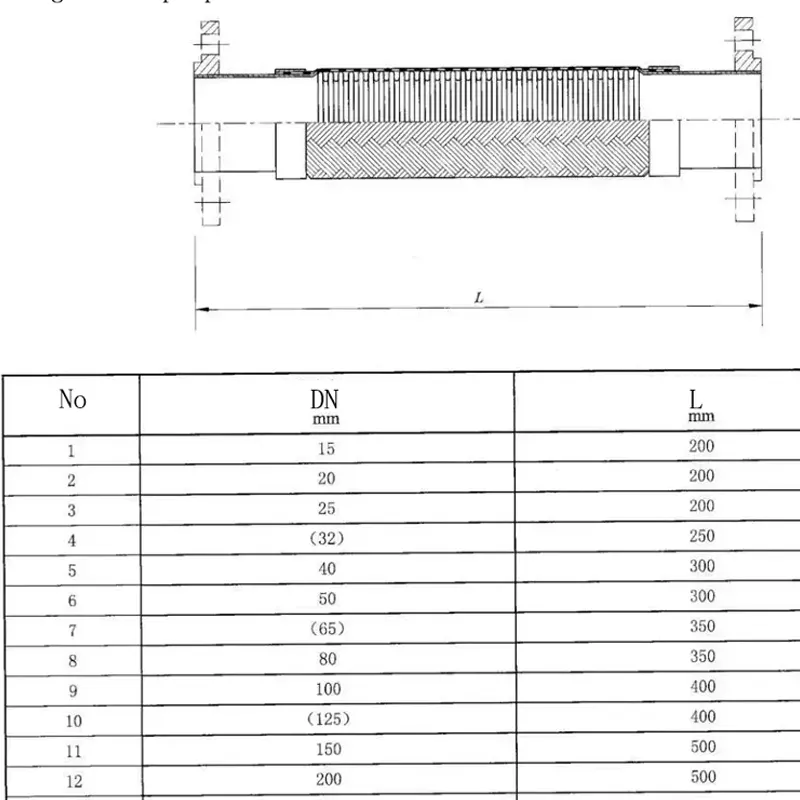
In the world of pipe systems, rubber expansion joints for pipes are unsung heroes. These flexible connectors, primarily made from elastomeric materials, are designed to absorb movement, isolate vibration, accommodate thermal expansion, reduce noise, and compensate for misalignment in piping systems.
Functions of Rubber Expansion Joints

Noise and Vibration Attenuation
The primary purpose of elastomeric expansion joints is to reduce noise and vibration while accommodating thermal movements in all directions. By introducing an intentional discontinuity between pipe materials, they interrupt the transmission path of sound and vibration. Any rotating equipment—such as centrifugal pumps—generates noise and vibration due to unbalanced forces. The frequency and amplitude depend on pump speed and type. An elastomeric expansion joint dampens these disturbance frequencies and absorbs energy, minimizing the transmission of noise, vibration, and stress to adjacent piping or equipment.
Accommodating Multi-Directional Thermal Movement
The flexible body of an expansion joint also accepts thermal movement in every direction (see Fig. 1). In any system design, thermal movement is a critical consideration. Depending on temperature variation, material, and pipe length, thermal growth can produce forces that quickly exceed allowable stress in the piping. Expansion joints allow axial compression and extension, lateral offset, torsion, and angular deflection, thereby absorbing thermal stress.
Impact/Wear Resistance and Misalignment Compensation
Elastomeric expansion joints are widely used for their excellent impact resistance and abrasion performance. Water hammer, pressure surges, and seismic events impose shock and bending loads on piping systems. An expansion joint behaves like a shock absorber to withstand these forces and displacements, protecting the system from damage. In addition, elastomers offer outstanding wear resistance and fatigue endurance—often superior to metallic elements. Pipe misalignment is common in new builds and retrofits; expansion joints compensate for misalignment and provide a forgiving connection between piping and equipment. With advances in synthetic rubbers and reinforcement fabrics, many products now handle up to 350 psi and 400 °F—service conditions that previously excluded non-metallic materials.
Types and Configurations of Rubber Expansion Joints
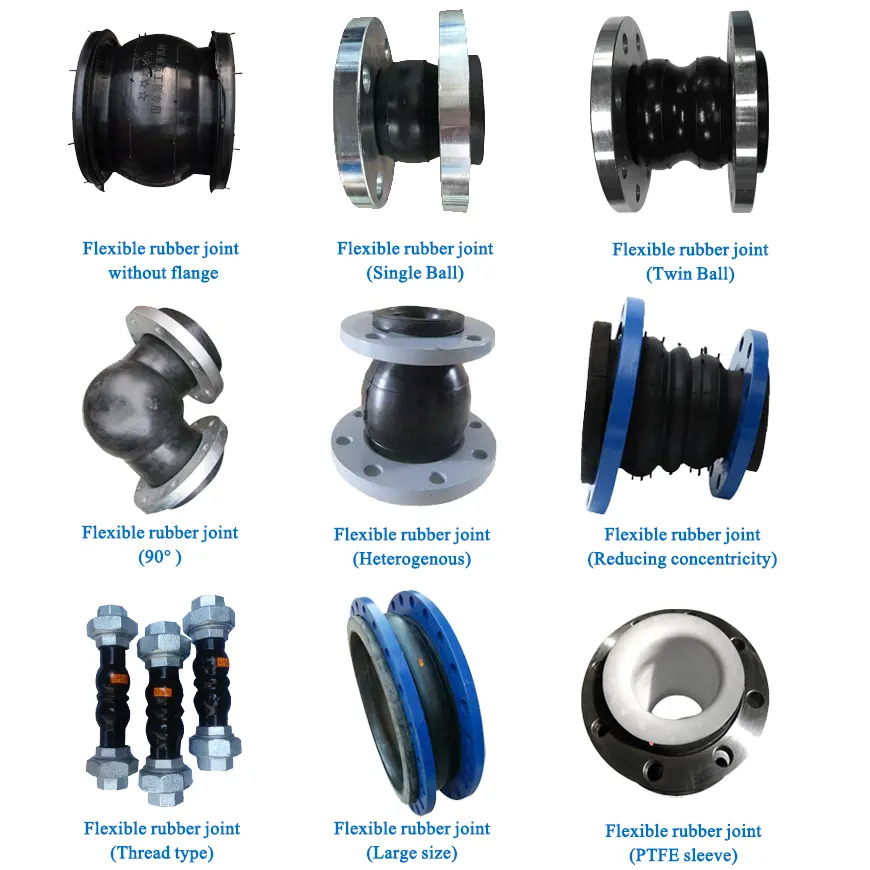
- By geometry: concentric equal-diameter, concentric reducer, eccentric reducer.
- By structure: single-sphere, double-sphere, elbow sphere.
- By connection: flanged, threaded, threaded-pipe–to-flange.
- By pressure rating: 0.25 MPa, 0.6 MPa, 1.0 MPa, 1.6 MPa, 2.5 MPa.

Applications of Rubber Expansion Joints
Building Services
- Water supply & drainage: Compensate thermal expansion/contraction and pipe movement in high-rise systems, reducing leakage risk.
- Ventilation systems: Connect ducts, absorb fan vibration, and lower noise.
Chemical Industry
- Corrosive media transfer: Resistant to acids, alkalis, and salts for safer operations.
- Gas transfer: Provide sealing and support to prevent leakage.
Metallurgy
- High temperature/pressure: Withstand severe service and stabilize production equipment.
- Condensate systems: Compensate thermal movement and protect piping and equipment.
Water & Wastewater
- WWTPs: Handle sewage and sludge lines with corrosion and abrasion resistance.
- Municipal water: Improve water quality assurance by reducing vibration and noise.
Oil & Gas
- Pipeline transfer: Oil-resistant and high-temperature capable for long-distance connections.
- Refineries: Compensate equipment vibration and pipe movement, improving reliability.
HVAC
- Chilled/Hot water lines: Isolate pump and fan vibration to enhance comfort.
- Duct connections: Provide flexibility to suit changing layouts and space constraints.
Fire Protection
- Fire mains: Enable quick install/removal for emergency needs while accommodating pipe movement.
Power Generation
- Cooling water: High-temperature and high-pressure capability for plant CW systems.
- Steam lines: Absorb thermal stresses and help prevent pipe rupture.
By absorbing vibration, compensating displacement, and providing sealing, rubber expansion joints are indispensable across industrial and commercial piping systems.
Key Considerations for Selection
- Service Conditions
- Media: Identify fluid type (water, oil, acids/alkalis, steam). Match elastomer to chemistry—e.g., EPDM or FKM for corrosive media; NBR for oils.
- Pressure: Select a pressure class to meet design pressure and expected surges (consider upsizing when fluctuations are significant).
- Temperature: Typical ranges: NR ~70–100 °C; CR ~100–130 °C; EPDM ~130–150 °C; FKM ~150–200 °C.
- Size & Connections
- Nominal diameter: Match the pipe DN (typical range DN32–DN3000) to ensure seal integrity and stability.
- Connection type: Flanged for large sizes/frequent removal; threaded for small sizes; welded transitions where sealing is critical.
- Elastomer & Performance
- Material selection: NR for general elasticity; EPDM for heat/acid/alkali resistance; FKM for aggressive chemicals; NBR for oils.
- Key properties: Elasticity for vibration/movement, abrasion resistance for life, and aging resistance for long-term stability.
- Form Factor & Type
- Single vs. double sphere: Single offers simplicity; double provides greater movement capability.
- Reducers: Concentric/eccentric reducers for transitions between pipe sizes.
- Special forms: Beaded/flanged soft joints, rubber elbows, rubber tees as layout requires.
- Flange Materials
- Carbon steel: Cost-effective for general environments with adequate pressure capability.
- Stainless steel: Superior corrosion/high-temperature resistance for harsh service.
- Geometry & Installation
- Face-to-face length: Choose a structural length that fits layout and service movement.
- Installation notes: Install in a neutral, untwisted state; tighten flange bolts evenly; use anchors/guides/limit rods at pump discharges, high-pressure lines, or tall buildings.
Conclusion
Rubber expansion joints enhance the safety, efficiency, and longevity of piping systems. By providing flexibility and shielding against common mechanical stresses, they are a critical component across many industries.